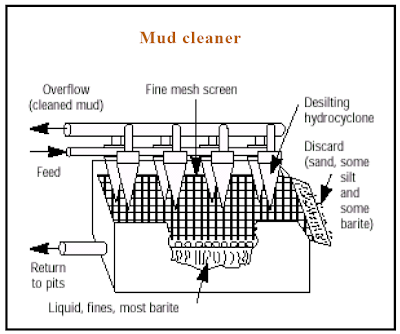
Surface pumping systems are ideal for injection and many other high-pressure applications. SPS incorporate the most dependable downhole component of any ESP. For pumping element, an SPS comprise industry standard electric motors: fifty and sixty hurts to pull speed, low in medium voltages, NEMA, above NEMA and I.E.C motor frames. The customer preferred brand in closure or bearing type and any available motor options can be accommodated. Natural gas or diesel engine driven SPS can be supplied for remote locations without a convenient electric supply. The motor is connected to the bearing housing or thrust chamber via an industry standard grade or gear style flexible coupling. One front in two rear ball bearings are lubricated by oil rings as shown in video. This method minimizes the volume of oil in the housing which in turn reduces operating temperature and extends run times. The bearing housing has a small number of moving parts and requires only occasional oil changes. Bearing housing modules can be replaced on location with minimum downtime. An adapter is located between the bearing housing and the suction chamber; this provides a physical opened atmosphere separation between the pumped fluid and the bearing housing.

In the event of leakage of pump fluid from the suction chamber, fluid would be expelled through openings in the adapter and would not enter the bearing housing. Also shown in the video, a separate step shaft is bolted to the end of the bearing shaft by incorporating this step shaft. Replacement of the shaft is possible without having to replace the entire bearing housing. The suction chamber design provides minimal restriction to flow to assist suction or N.P.S.H. characteristics. SPS requires only one mechanical seal which is located in the optimum location within the suction chamber. The seal is exposed only to suction pressure. A wide variety of mechanical seals are available to suit the application and suction pressures up to three thousand psi. Single, double, and tandem API 682 cartridge seals with appropriate API flush and quench plans are available.
Cartridge designs incorporate would group patented front pullout design which simplifies seal replacement and reduces downtime. Between the suction chamber in the pump element, a pump adaptor and a spline pump coupling facilitate access for easy replacement of mechanical seals. The pumping element is the heart of the surface pumping and many sizes are available to match flow and pressure requirements. Various configurations of material options are offered to ensure compatibility with corrosive and erosive liquids or liquefied gases. Pump elements are supplied as modules with bolted connections and spline shaft and they can be easily replaced in the field. The discharge had bolts onto the pump element and his size to suit flow and maximum discharge pressure. Standard connections to customer piping is via an ANSI B16.5 lap raised face or RTJ flange to simplify flange to flange alignment. All SPS components are mounted onto a patented skid which has been designed to capitalize on the flexibility of SPS multistage centrifugal pump technology. The skid is easily modified to accommodate any future changes to the motor and pump.
The oil production process described is continuous and the operation of all the downhole pumps depends on the reliability of the surface injection pump. Since the late 1980s, producers have increasingly chosen to use the proven and dependable downhole pump technology for surface pumps over older technologies such as reciprocating plunger and split case centrifugal pumps. Producers are embracing the benefits of ESP's SPS surface pumping systems, reliability, extremely low a lifetime cost, minimal routine maintenance, negligible downtime during necessary repairs, and flexibility for changing operating conditions. The same benefits proven in oil production make the SPS ideal for a wide variety of high pressure pumping applications such as jet pump power fluid, mine dewatering, dust suppression long wall hydraulics, pipeline booster and gas services such as CO2, NGL, and LPG.