Post recommended by Eng. Mohamed Fathy, the author of this post and special thanks for his efforts in enrichment our blog
Function Of Unit
Converts low octane number naphtha into high octane gasoline product on continuous basis as basis as the catalyst is continuously regenerated in the CCR section.
Involved Reactions
Dehydrogenation of Naphthenes
Isomerisation of Naphthenes and Paraffins
Dehydrocyclization of Paraffins
Hydrocracking
Demethylation
Dealkylation of Aromatics
Platforming Catalyst
Platforming catalyst is Bifunctional type which has:
• Acidfunction
– Responsible for Naphthenes Isomerisation and provided by Chloride Injection
• Metalfunction
– Responsible for Dehydrogenation and Dedydrocyclization provided by the metalsites
Platforming Reactions
Unit Feed Stocks
Hydrotreated heavy naphtha having the following specs.:
Total Sulfur : <0.5 wt-ppm
Total Nitrogen: <0.5 wt-ppm
Distillation End Point : 204 °C (max)
Lead: 20 wt-ppb (max)
Arsenic: 1 wt-ppb (max)
Iron: 1 wt-ppm(max)
Copper + Heavy Metals: 25 wt-ppb (max)
Fresh Feed Quality
Feed with high EP (above 204 °C) are difficult to reform and cause high catalyst coking rate.
Sulphur content above 0.5 ppm will cause temporary poisoning for platinum and lower catalyst activity.
Higher nitrogen content (above 0.5 ppm) will cause loss of acid site activity although hydrogen production will increase.
Product Specifications
Plateformer Material Palance
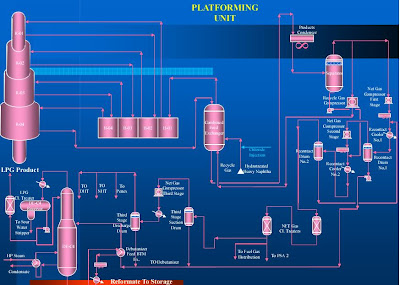
ProcessFlow Diagram
Platforming Section
PLATFORMING UNIT
Plate Exchanger Advantages
Less capital outlay.
lower installation cost (piping, space,…..)
Higher thermal efficiency
Extensive heat exchange area in a single compact unit
Low pressure drop
Range between 0.35-1.5 barg
Low operating cost
less fouling, fewer flanges, accessibility for maintenance through top and bottom manway
PLATE HEAT EXCHANGER SIMPLIFIED OPERATIONS
PLATE HEAT EXCHANGER
DISTRIBUTION HEADER DETAILED DESIGN
Platforming Process Variables
Reactor
Temperature• Reactor Inlet
– Is the major parameter used to meet product quality requirements
• Temperature Difference
– Represents amount of reactions performed in each reactor
Liquid Hourly Space Velocity
LHSV(hr-1) = { volume of feed (/hr) } / { volume of catalyst in Reactors }
**The higher space velocity (lower Residence Time), the lower product RON.
**Increased Reactor Temperatures will offset this effect.
Reactor Pressure
Decreasing reactor pressure will :
•Increase hydrogen and reformate yield
•Decrease temperature requirement to achieve target Octane Number
•Increase catalyst coking rate
Hydrogen/Hydrocarbon Ratio
Increasing Hydrogen/Hydrocarbon Ratio will :
•Increase temperature requirement to achieve target RON
•Decrease catalyst cokingrate
H2/HC Ratio = { RG Purity X Recycle Gas Rate, Kmol/hr } / { Fresh Feed, Kmol/hr }
Reactor
The catalyst flows by gravity out from Reactor bottom to the top of the next reactor. Through catalyst Transfer pipe Catalyst continues to flow through each reactor flow through each reactor until it again reaches the bottom of the last reactor.
This completes the transfer circuit. Catalyst flow between the reactors is through equally-spaced transfer lines designed to ensure uniform catalyst flow through the catalyst bed.
















I can see that you are an expert at your field! I am launching a website soon, and your information will be very useful for me.. Thanks for all your help and wishing you all the success in your business.
ReplyDeleteמדביר מקצועי